General Organic Chemistry Class 11 Pdf To Jpg

Soil - Wikipedia. Soil is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and countless organisms that together support life on Earth. Soil is a natural body called the pedosphere which has four important functions: it is a medium for plant growth; it is a means of water storage, supply and purification; it is a modifier of Earth's atmosphere; it is a habitat for organisms; all of which, in turn, modify the soil. Soil has been called the Skin of the Earth.
- Here you can download FREE 10th class Chemistry notes in PDF for the Punjab Board students, and the solution of Carvan Book, and you can view online without.
- View the most recent ACS Editors' Choice articles from Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. See all Journal of Medicinal Chemistry ACS Editors' Choice articles.
- BibMe Free Bibliography & Citation Maker - MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard.
- View Notes - Chemistry Whitten 10th Edition 2014 Intructor's Solution Manual from CHEMISTRY CHM 1045 at Miami Dade College, Miami. IM10-01 (9-9).pdf IM10-02 (9-15.
- Chapter 6 OxidatiOn-reduCtiOn reaCtiOns 207 6.1 An Introduction to Oxidation- Reduction Reactions 6.2 Oxidation Numbers 6.3 Types of Chemical.
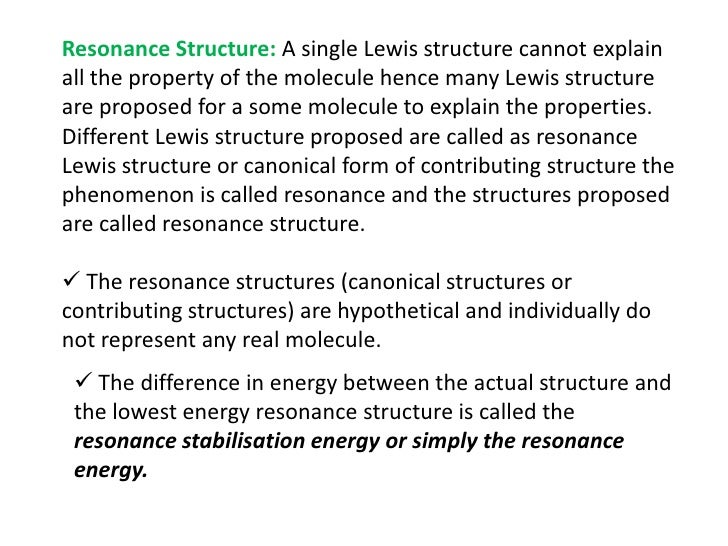
Remember: Seeing this.
Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness soil has been considered as an ecosystem by soil ecologists. Edaphology is concerned with the influence of soils on living things. The world's ecosystems are impacted in far- reaching ways by the processes carried out in the soil, from ozone depletion and global warming, to rainforest destruction and water pollution. With respect to Earth's carbon cycle, soil is an important carbon reservoir, and it is potentially one of the most reactive to human disturbance. A gram of soil can contain billions of organisms, belonging to thousands of species, mostly microbial and in the main still unexplored. This ventilation can be accomplished via networks of interconnected soil pores, which also absorb and hold rainwater making it readily available for plant uptake.
Soil is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and countless organisms that together support life on Earth. Soil is a natural body called the. Sulfur or sulphur (see spelling and etymology) is a chemical element with symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent, and nonmetallic. Download physics formulas and concept pdf for class 11, 12, IITJEE, PMT and other competetive exams. It is concise and contain all formulas. 249 Responses to “Some Very Peculiar NMR Spectra in Organic Letters” mumm Says: August 19th, 2013 at 2:51 AM. I guess that the spectra was processed by the.
Since plants require a nearly continuous supply of water, but most regions receive sporadic rainfall, the water- holding capacity of soils is vital for plant survival. The biological influences on soil properties are strongest near the surface, while the geochemical influences on soil properties increase with depth. Mature soil profiles typically include three basic master horizons: A, B and C. Backup Steam Games For Reinstall Chrome more.
The solum normally includes the A and B horizons. The living component of the soil is largely confined to the solum, and is generally more prominent in the A horizon. The soil texture is determined by the relative proportions of the individual particles of sand, silt, and clay that make up the soil. The interaction of the individual mineral particles with organic matter, water, gases via biotic and abiotic processes causes those particles to flocculate (stick together) to form aggregates or peds. Since soil water is never pure water, but contains hundreds of dissolved organic and mineral substances, it may be more accurately called the soil solution. Water is central to the dissolution, precipitation and leaching of minerals from the soil profile. Finally, water affects the type of vegetation that grows in a soil, which in turn affects the development of the soil, a complex feedback which is exemplified in the dynamics of banded vegetation patterns in semi- arid regions.
These bound nutrients interact with soil water to buffer the soil solution composition (attenuate changes in the soil solution) as soils wet up or dry out, as plants take up nutrients, as salts are leached, or as acids or alkalis are added. Soil p. H is a function of many soil forming factors, and is generally lower (more acid) where weathering is more advanced. Some nitrogen originates from rain as dilute nitric acid and ammonia.
Once in the soil- plant system, most nutrients are recycled through living organisms, plant and microbial residues (soil organic matter), mineral- bound forms, and the soil solution. Both living microorganisms and soil organic matter are of critical importance to this recycling, and thereby to soil formation and soil fertility. Throughout history, civilizations have prospered or declined as a function of the availability and productivity of their soils.
From the fall of Rome to the French Revolution, knowledge of soil and agriculture was passed on from parent to child and as a result, crop yields were low. During the European Dark Ages, Yahya Ibn al- 'Awwam's handbook. His famous book Le Th. His conclusion came from the fact that the increase in the plant's weight had apparently been produced only by the addition of water, with no reduction in the soil's weight. Others concluded it was humus in the soil that passed some essence to the growing plant.
Still others held that the vital growth principal was something passed from dead plants or animals to the new plants. At the start of the 1. Jethro Tull demonstrated that it was beneficial to cultivate (stir) the soil, but his opinion that the stirring made the fine parts of soil available for plant absorption was erroneous. The French chemist Antoine Lavoisier showed in about 1. The enrichment of soil with guano by the Incas was rediscovered in 1.
Alexander von Humboldt. This led to its mining and that of Chilean nitrate and to its application to soil in the United States and Europe after 1. In England John Bennet Lawes and Joseph Henry Gilbert worked in the Rothamsted Experimental Station, founded by the former, and (re)discovered that plants took nitrogen from the soil, and that salts needed to be in an available state to be absorbed by plants. Baixar O Filme Sherlock Holmes 1 Dublado Rmvb Player. Their investigations also produced the . This led to the invention and use of salts of potassium (K) and nitrogen (N) as fertilizers. Ammonia generated by the production of coke was recovered and used as fertiliser.
However, the dynamic interaction of soil and its life forms still awaited discovery. In 1. 85. 6 J. Thomas Way discovered that ammonia contained in fertilisers was transformed into nitrates. The symbiosis of bacteria and leguminous roots, and the fixation of nitrogen by the bacteria, were simultaneously discovered by the German agronomist Hermann Hellriegel and the Dutch microbiologist Martinus Beijerinck. Crop rotation, mechanisation, chemical and natural fertilisers led to a doubling of wheat yields in western Europe between 1. Studies concerning soil formation. However, soil is the result of evolution from more ancient geological materials, under the action of biotic and abiotic (not associated with life) processes. After studies of the improvement of the soil commenced, others began to study soil genesis and as a result also soil types and classifications.
In 1. 86. 0, in Mississippi, Eugene W. Hilgard studied the relationship among rock material, climate, and vegetation, and the type of soils that were developed. He realised that the soils were dynamic, and considered soil types classification. At the same time Vasily Dokuchaev (about 1. Russia who conducted an extensive survey of soils, finding that similar basic rocks, climate and vegetation types lead to similar soil layering and types, and established the concepts for soil classifications. Due to language barriers, the work of this team was not communicated to western Europe until 1. German by Konstantin Dmitrievich Glinka, a member of the Russian team.
Marbut was influenced by the work of the Russian team, translated Glinka's publication into English. National Cooperative Soil Survey, applied it to a national soil classification system. Soil is said to be formed when organic matter has accumulated and colloids are washed downward, leaving deposits of clay, humus, iron oxide, carbonate, and gypsum, producing a distinct layer called the B horizon. This is a somewhat arbitrary definition as mixtures of sand, silt, clay and humus will support biological and agricultural activity before that time.
These constituents are moved from one level to another by water and animal activity. As a result, layers (horizons) form in the soil profile. The alteration and movement of materials within a soil causes the formation of distinctive soil horizons. However, more recent definitions of soil embrace soils without any organic matter, such as those regoliths that formed on Mars.
Soil development would proceed most rapidly from bare rock of recent flows in a warm climate, under heavy and frequent rainfall.